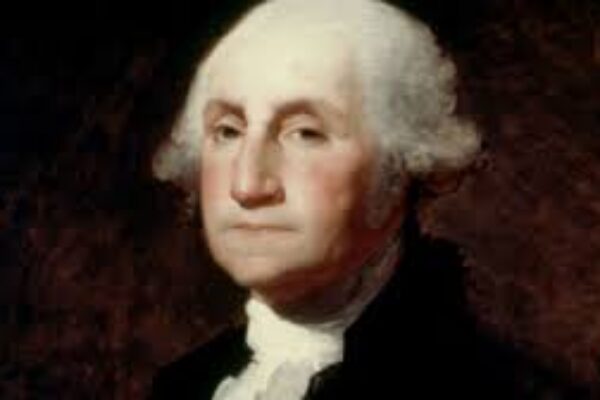
On March 15, 1783, in Newburgh, New York, Washington gave the greatest performance of his career in order to head off a conspiracy that might have led to military government. This was after the victory at Yorktown but before the final signing of the Treaty of Paris in September.
The Congress of that day — the Congress of the Confederation — was less effective than the Congress of our own time, because it could not levy taxes to pay troops. Because of this, many officers believed that this Congress could not — should not — govern the new country. As such, some in the army wanted Washington to take over as a sort of monarch (flattering but unappealing to America’s first president) while others wanted to overthrow Congress altogether. Washington got wind of what had the potential to be our nation’s first coup and delivered an extraordinary speech — entirely his own writing.
Either before or during the speech, we are told that he took out a pair of glasses, which no one had ever seen him wear before. “Gentlemen,” he said, “you will permit me to put on my spectacles, for I have not only grown gray, but almost blind in the service of my country.”
This piece of theater brought tears to the eyes of some of the officers. It probably had a deeper effect on his audience than the content of his speech, which was strong and heartfelt. He showed his empathy for his military officers by reminding them of his longstanding ties to the army:
If my conduct heretofore, has not evinced to you, that I have been a faithful friend to the Army, my declaration of it at this moment wd. be equally unavailing and improper. But as I was among the first who embarked in the cause of our common Country. As I have never left your side one moment, but when called from you on public duty. As I have been the constant companion and witness of your Distresses, and not among the last to feel, and acknowledge your Merits.
He ended with this stirring conclusion:
And let me conjure you, in the name of our Common Country, as you value your own sacred honor, as you respect the rights of humanity, and as you regard the Military and National Character of America, to express Your utmost horror and detestation of the Man who wishes, under any specious pretences, to overturn the liberties of our Country, and who wickedly attempts to open the flood Gates of Civil discord, and deluge our rising Empire in Blood.
The danger of civil war between Congress and the army was real, but Washington easily won over the army with his theatrical gesture of the new spectacles and his passion for liberty as he expressed it in his speech.
But these would not have been so effective if it were not for Washington’s character. For all his faults (as a slaveholder and land speculator, he certainly had faults), he had established a reputation for courage and integrity. People trusted him. His audience knew him well enough to see that he truly believed in what he said.
Above all, he was a leader who could step back from power, as he did on a number of occasions. How many men who have commanded armies of liberation have declined offers of monarchial power? And how many military commanders have refused to lead an underpaid army against its government? Julius Caesar was one of many Roman commanders who led their disgruntled armies into the civil wars that destroyed the Roman Republic. Washington knew that history.
Great threats call for great theater, and great theater can adorn great truths. Although he was a showman, Washington was truly sincere; he really did believe in freedom and in the subordination of the military to civilian government. And although he had always had magnificent ambitions, he knew where ambitions might lead if they are unbridled — to a tyranny that would destroy the freedom he had been fighting for. And so he restrained his ambitions and buried them behind the face of leadership.
Paul Woodruff is a professor of philosophy at The University of Texas at Austin.
A version of this op-ed appeared in the Dallas Morning News.